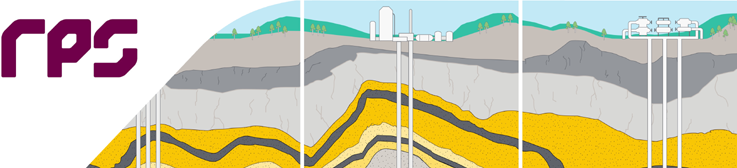
The following four courses (SPC5030, SPC5031, SPC5032 & SPC5038) will provide participants with an awareness and understanding of subsurface CO2 storage, CO2 flow in the subsurface, and the key issues of reservoir depth, well design, reservoir lithology and quality, in relation to CCUS. SPC5030 will provide participants with an awareness and understanding of the subsurface needs of CCS projects. It will establish basics such as how much CCS is needed to make a difference to global warming and explore the types of CO2 injection. SPC5031 will address the awareness and understanding of subsurface CO2 storage volumetrics, CO2 flow in the subsurface away from injector wells, the objective of permanent and safe storage of CO2, and the key issues of reservoir depth, well design, reservoir lithology, reservoir quality, and reservoir architecture. SPC5032 will consider the range of potential leakage mechanisms that need to be assessed. It will include a detailed consideration of the monitoring strategies available to assure the safety and integrity of the CO2 storage site. Finally, SPC5038 will explore the petrophysical aspect of carbon capture and storage including capillary pressures, monitoring C02 plumes and the application of pulsed neutron logs.
SPC5030 - Fundamentals of CCS
CO2 in the atmosphere and options to cut CO2 emissions
This module outlines the history of greenhouse gases, explores CO2 emissions and how CO2 emissions can be cut. Learning outcomes include; an understanding of why we need to reduce the CO2 in the Earth's atmosphere, a realisation of the timescales we need to follow to cut greenhouse gas emissions, an appreciation of where the emitted CO2 derives from, and finally you will develop an understanding of where carbon capture and storage fits into the range of strategies that are being adopted to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
Estimated time: 60mins
Geological CCS, CCS as mitigation strategy
This module outlines geological storage options for CO2 and CCS as a mitigation strategy. Learning outcomes include understanding the main geological options for CCS, develop an appreciation of the objectives of geological (and engineering) activities required during CCS projects. You will also start to develop an appreciation of the CCS projects developed so far, how much CO2 is currently locked away annually and how much more CO2 must be locked up annually to mitigate global warming and finally appreciate the range of industrial activities that need to engage with CCS and knowledge some of the main CCS projects in operation.
Estimated time: 60mins
CO2-EOR and CCS: fate of CO2 in the subsurface
The aim of this module will primarily be to look at CO2 injection projects related to enhanced oil recovery, and the fate of CO2 in the subsurface. By the end of this module you will be able to appreciate what CO2-Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) is, and to acknowledge the planned role of CO2 hubs and clusters to facilitate large-scale CCS. You will start to understand storage capacity for CO2 (in a depleted oil field), as well as understand what happens to CO2 when it is injected into the subsurface and appreciate that CO2 injections rates are unlikely to be constant and that the injected gas may not be pure CO2.
Estimated time: 60mins
CO2 phase behaviour and properties, CO2 trapping
The aim of this module will be to examine how CO2 occurs in CCS sites and how phase behaviour is associated with pressure, temperature and water salinity. The module will also expand on CO2 characteristics to appreciate what happens to water chemistry at high CO2 pressures, in addition to understanding how CO2 becomes trapped in the subsurface despite its buoyancy compared to water.
Estimated time: 60mins
SPC5031 - Geological Storage of CO2
CO2 storage volumes and controls on porosity in sandstone reservoirs
Over the duration of this module, we will explore a range of depositional, early diagenetic, and burial diagenetic factors that influence reservoir properties in sandstone reservoirs. As we explore these primary (deposition) and secondary (early and burial diagenesis) factors you will gain an appreciation of the reasons for porosity in sandstone reservoirs. Finally, we will explore the range and types (primary or secondary) of porosity in sandstone reservoirs.
Estimated time: 60mins
CO2 storage volumes and controls on porosity in carbonate reservoirs
During this module, we will explore a range of depositional, early diagenetic, and burial diagenetic factors that influence reservoir properties in carbonate reservoirs. As we explore these primary (deposition) and secondary (early and burial diagenesis) factors you will gain an appreciation of the reasons carbonate reservoirs tend to have lower porosity than sandstone reservoirs. Finally, we will explore the range and types (primary or secondary) of porosity in carbonate reservoirs.
Estimated time: 60mins
Risk and rate of mineral dissolution due to CCS: calcite in sandstones and limestones
Over the duration of this module, we will explore the risks and rates of mineral dissolution due to carbon capture and storage. Our focus will be primarily on the dissolution risk of carbonate minerals in sandstones and limestones, but we will also discuss other minerals. We will discuss dissolution modeling and how these techniques can be used to enhance our understanding of CCS project risks. Finally, we will look at some field and lab based examples where dissolution has been caused by CCS.
Estimated time: 60mins
CO2 storage efficiency
This module will explore the phenomenon known as CO2 storage efficiency. CO2 storage efficiency is a very important parameter that controls how much carbon dioxide can be stored at any given site in the subsurface. We will discuss the factors that affect storage efficiency and how these factors vary in saline aquifers and depleted oil and gas fields. Finally, we will discuss some methods to determine CO2 storage efficiency.
Estimated time: 60mins
SPC5032 - Behaviour of CO2 in Reservoirs
Injectivity at CCS sites and controls on permeability in potential CCS reservoirs
Over the duration of this module, we will explore the factors that influence injectivity at a CCS project, most importantly permeability. As permeability is the master control on the injectivity of a CCS project we will discuss the various factors that control reservoir permeability. Finally, we will focus on the influences of rock texture, specifically pore throat radius and sorting, have on reservoir permeability.
Estimated time: 60mins
Relative permeability, formation damage, history matching CO2 flow patterns
The aim of this module will be to learn about how CO2 interacts with other elements of the subsurface, such as other fluids and stratigraphy. Understand the role of two-phase flow and relative permeability in influencing CO2 movement in mixed brine-CO2 systems and develop an appreciation of the various processes that can lead to formation damage and thus a reduction of CO2 injectivity through examples.
Estimated time: 60mins
Geomechanical responses to elevated CO2 pressure
This module will develop an appreciation of the geomechanical issues around the CCS lifecycle, including how the magnitudes and orientations of the three principle stresses have a major influence on the consequences of injecting CO2 into the subsurface. We will also explore how to understand the risks of failure mechanisms and the link between elevated CO2 pressure and movement on existing fault zones.
Estimated time: 60mins
Risk and rate of mineral precipitation: halite and water salinity plus CCS in basalt
Over the duration of this module, we will explore the risks and rates of mineral precipitation due to carbon capture and storage. We will discuss the mineral growth in conventional sandstone and limestone, and unconventional basalt, reservoirs and limestone. Additionally, we will talk about the risk of hyalite growth and the effects of water salinity on carbon capture and storage projects.
Top-seal properties and stability at CCS sites
In this module, you will learn about various top-seals or caprocks which can be used in a CCS project. Understand how different top seals will need different approaches to understand their lithologies. As well as develop an awareness of how the overall lithology plays a part in the top seal effectiveness.
Estimated time: 60mins
SPC5033 - Monitoring CO2 Storage
CO2 risk of leakage from CCS sites and borehole issues
In this module, you will learn about CO2 leakage risks from CCS sites, focussing initially on generalities, then moving on to leakages through intact-top seals and leakage via old wells. Appreciate loss of CO2 to atmosphere and understand that top seal effects, well effects, and fault and fracture effects can conceivably all lead to escape of CO2.
Estimated time: 60mins
CO2 leakage associated with geomechanical issues
In this module, you will learn about the negative impacts associated with a pressure increase from CO2 injection, including the fracturing of top-seals, reactivation of faults and induced seismicity as well as ground surface deformation and uplift.
Estimated time: 60mins
Monitoring and risk assessment of CCS projects
In this module, you will learn about various monitoring techniques for CCS projects along with the benefits and drawbacks of each. This module will also cover multiple case studies that have implemented these techniques along with risk assessment factors that need to be considered for any CCS project.
Estimated time: 60mins
SPC5038 - Petrophysics for CCS
Physical Chemistry of CO2
This module outlines the most important basic physio-chemical principles of CO2, and where they are needed in CCUS. The module will cover the basic units and concept used in the CCUS industry and how they differ from the petroleum industry, before looking at the physical properties of CO2 and how environmental conditions affect its phase and its reactions to water.
Estimated time: 60mins
Petrophysics for CCUS
In this module, you will learn the properties of CO2 that affect log responses and the issue of how an immiscible fluid which is less dense than water distributes itself in a suitable trap. Understand the bonds between molecules and the relationship between the fluids and solid grains in the reservoir.
Estimated time: 60mins
Capillary Pressure for CCUS
This module explains the fundamentals of capillary pressure and how to interpret capillary pressure curves. Explore the differences between CO2 and methane in terms of their interfacial tension and density, before looking at the effect of CO2 on the permeability of the reservoir.
Estimated time: 60mins
Monitoring CO2 plumes in the subsurface
This module explores wireline logs and how they are used to monitor the movement of CO2 once it is injected into the subsurface. We will look at the design of observation wells and injection wells to understand how they facilitate the monitoring of CO2 and how their construction can affect measurements.
Estimated time: 60mins
Example Learning Outcomes
- Appreciate the types of CO2 injection projects that have occurred so far, and the ones that are planned.
- Discuss CCS projects that have been a success and those that have had problems.
- Build awareness of the reservoir rocks that store CO2 and the volumetrics of CO2 storage.
- Acknowledge the importance of the storage efficiency factor in controlling how much CO2 can be injected.
- Gain an appreciation of the question of the injectivity of CO2 and the roles of permeability and aquifer architecture on CO2 flow.
KeyFacts Energy Industry Directory: RPS Energy l KeyFacts Energy news: Training
 KEYFACT Energy
KEYFACT Energy